Bacterial Identification Dichotomous Key Generator
- Bacterial Identification Dichotomous Key Generator Key
- Insect Identification Dichotomous Key
- Dichotomous Key Template
- Plant Identification Dichotomous Key
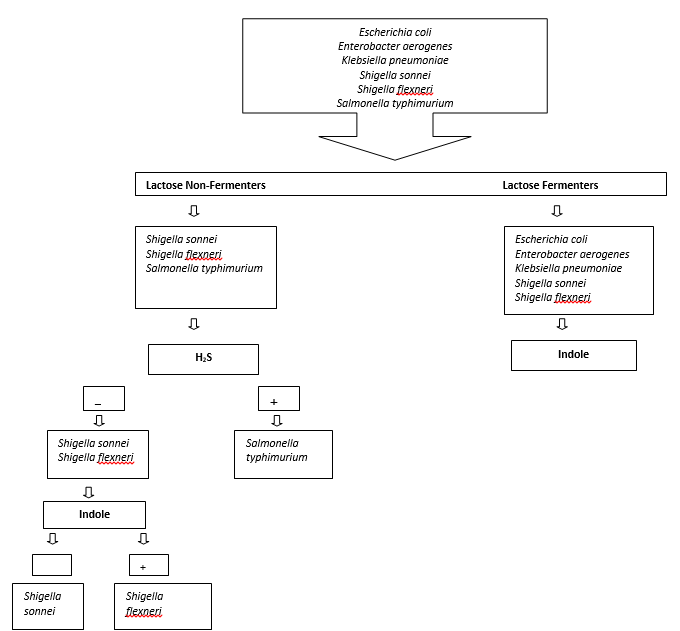
Dichotomous Key/Bacteria. From Wikibooks, open books for an open world Dichotomous Key. Jump to navigation Jump to search. Include the cyanobacteria (autotrophic. Feb 28, 2018 Creating a dichotomous key: Phenetic identification of bacteria-Part 2 Microbial Zoo. Identification of unknown bacteria using dichotomous key-Part 1. Bacterial Colony Description.
Bacterial Identification Dichotomous Key Generator Key
Sims 4 license key generator online no survey. Include the cyanobacteria (autotrophic) and eubacteria (heterotrophic).
Insect Identification Dichotomous Key
- Acidobacteria (acidophilic, gram positive, high G+C, common in dirt)
- Actinobacteria (high G+C gram positive bacteria)
- Aquificae (hyperthermophilic chemolithoautotrophs, gram negative)
- Bacteroidetes (really diverse group with pathogens, commensals, and free-living bacteria; anaerobic, gram negative, rod shaped)
- Chlamydiae (obligate intracellular parasites of eukaryotic cells, gram negative)
- Chlorobi (anaerobic, photoautotrophic, gram negative green sulfur bacteria)
- Chloroflexi (greeen nonsulfur bacteria)
- Chrysiogenetes (chemolithoautotrophic bacterium)
- Cyanobacteria (oxygenic photosynthetic bacteria and chloroplasts)
- Deferribacteres (aquatic, anaerobic bacteria)
- Deinococcus-Thermus (extremophiles, gram negative)
- Dictyoglomi (thermophilic chemoorganotrophs)
- Fibrobacteres (cellulose digesting, anaerobic rumen bacteria, two species)
- Firmicutes (low G+C gram positives)
- Fusobacteria (obligate anaerobic heterotrophs, many involved in human infections, gram negative, non-spore forming)
- Gemmatimonadetes (Gram negative bacteria lacking DAP in cellular envelopes)
- Nitrospira (gram negative; includes nitrite-oxicizers, thermophilic sulfate reducers, and acidophilic iron reducers)
- Planctomycetes (ovoid gram negative bacteria, reproduce by budding)
- Proteobacteria (purple bacteria and relatives, gram negative)
- Spirochaetes (spiral-shaped chemoheterotrophs, gram negative)
- Synergistetes (gram negative, rod/vibroid cell shape)
- Tenericutes (gram positive, no cell wall)
- Thermodesulfobacteria (thermophilic, sulfate-reducing bacteria)
- Thermomicrobia (hyperthermophilic chemoheterotrophs)
- Thermotogae (hyperthermophilic, obligate anaerobic, fermentive heterotrophs)
- Verrucomicrobia (terrestrial, aquatic, some associated with eukaryotic hosts; gram negative)
Dichotomous Key Template
Plant Identification Dichotomous Key
A related type of identification key, the polychotomous key, uses a similar question-and-answer branching format. How to Use a Dichotomous Key. Dichotomous keys allow their users to reliably identify objects in the natural world. Dichotomous keys are most often used for identifying plant and animal species based on their characteristics. Mar 10, 2018 Eubacteria are prokaryotes, which means they lack a nuclear membrane. Most have cell membranes and cell walls. Bacteria with thick cells walls are termed gram-positive because they're susceptible to dying during a test called the Gram stain. The Gram stain is the first test used in bacterial classification.